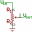
Berikut ini antar muka minimalis antara ESP32 dengan sensor lingkungan BMP280
Pin yang dipakai:
- VCC di ESP32 dihubungkan ke VCC di BMP280
- GND di ESP32 dihubungkan ke GND di BMP280
- SCL di ESP32 dihubungkan ke SCL di BMP280
- SDA di ESP32 dihubungkan ke SDA di BMP280
Software juga dibuat minimalis
// https://bitbucket.org/christandlg/bmx280mi/src/master/examples/BMx280_I2C/BMx280_I2C.ino
// BMx280_I2C.ino
//
// shows how to use the BMP280 / BMx280 library with the sensor connected using I2C.
//
// Copyright (c) 2018 Gregor Christandl
//
// connect the AS3935 to the Arduino like this:
//
// Arduino - BMP280 / BME280
// 3.3V ---- VCC
// GND ----- GND
// SDA ----- SDA
// SCL ----- SCL
// some BMP280/BME280 modules break out the CSB and SDO pins as well:
// 5V ------ CSB (enables the I2C interface)
// GND ----- SDO (I2C Address 0x76)
// 5V ------ SDO (I2C Address 0x77)
// other pins can be left unconnected.
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#define I2C_SDA 15
#define I2C_SCL 13
#include <BMx280I2C.h>
#define I2C_ADDRESS 0x76
//create a BMx280I2C object using the I2C interface with I2C Address 0x76
BMx280I2C bmx280(I2C_ADDRESS);
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(1000);
//wait for serial connection to open (only necessary on some boards)
while (!Serial);
// Wire.begin();
Wire.begin(I2C_SDA, I2C_SCL);
I2C_Scan() ; // just for verifying
//begin() checks the Interface, reads the sensor ID (to differentiate between BMP280 and BME280)
//and reads compensation parameters.
if (!bmx280.begin())
{
Serial.println("begin() failed. check your BMx280 Interface and I2C Address.");
while (1);
}
if (bmx280.isBME280())
Serial.println("sensor is a BME280");
else
Serial.println("sensor is a BMP280");
//reset sensor to default parameters.
bmx280.resetToDefaults();
//by default sensing is disabled and must be enabled by setting a non-zero
//oversampling setting.
//set an oversampling setting for pressure and temperature measurements.
bmx280.writeOversamplingPressure(BMx280MI::OSRS_P_x16);
bmx280.writeOversamplingTemperature(BMx280MI::OSRS_T_x16);
//if sensor is a BME280, set an oversampling setting for humidity measurements.
if (bmx280.isBME280())
bmx280.writeOversamplingHumidity(BMx280MI::OSRS_H_x16);
}
void loop() {
float temperature = 0;
float pressure = 0;
float humidity = 60; // default humidity
float co2 = 0;
float tvoc = 0;
delay(1000);
//start a measurement
if (!bmx280.measure())
{
Serial.println("could not start measurement, is a measurement already running?");
return;
}
//wait for the measurement to finish
do
{
delay(100);
} while (!bmx280.hasValue());
// Serial.print("Pressure: "); Serial.println(bmx280.getPressure());
// Serial.print("Pressure (64 bit): "); Serial.println(bmx280.getPressure64());
// Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.println(bmx280.getTemperature());
pressure = bmx280.getPressure();
temperature = bmx280.getTemperature();
//important: measurement data is read from the sensor in function hasValue() only.
//make sure to call get*() functions only after hasValue() has returned true.
if (bmx280.isBME280())
{
// Serial.print("Humidity: ");
// Serial.println(bmx280.getHumidity());
humidity = bmx280.getHumidity();
}
Serial.print("Temp\t");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print("Humidity\t");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print("Pressure\t");
Serial.print(pressure);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println("");
}
void I2C_Scan() {
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("I2C Scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for (address = 1; address < 127; address++ ) {
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0) {
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address < 16) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.println(address, HEX);
nDevices++;
}
else if (error == 4) {
Serial.print("Unknow error at address 0x");
if (address < 16) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.println(address, HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0) {
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
}
else {
Serial.println("done\n");
}
}